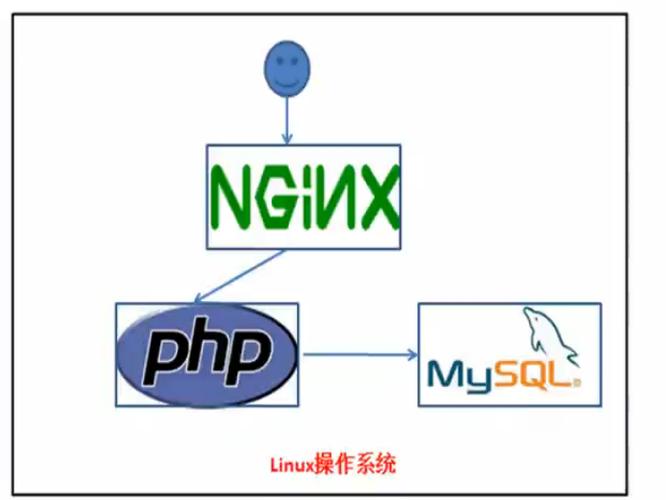
面向项目的学习是学习编码的最佳方法。Python是当今最需求的措辞,为了帮助您学习它,以下是一些您可以探索的最主要的Python项目:
Python游戏

Python图像编程

CIFAR10在Python中利用TensorFlow
开始看吧,和从开始到放弃说再见俗话说的好,没吃过猪肉还没见过猪跑?Python虽然对大多数小白来说,可能是从入门到放弃的过程。探究起来,可能初入门的同学没见到过Python俏丽的全景,一贯专一写hello world太多了,损失了对Python的爱才是放弃的紧张缘故原由吧。
在本文中,将用真实的代码给你展示从小白到大牛Python项目之旅。只要你敢看,我就敢写。开始吧!
只要你敢看,就敢让你成大牛您将学习如何按以下顺序创建这些Python项目:Python简介如何利用Python创建项目?我们可以用Python进行哪些项目?Python初学者项目:利用Python的Hangman游戏中级Python项目:在Python中数据可视化高等Python项目:利用Python进行机器学习结论
下面就开始这次从小白的大牛的Python代码盛宴。
Python简介Python是一种高等的,面向工具的,阐明性的编程措辞,已经引起了全天下的关注。Stack Overflow创造其38.8%的用户紧张在其项目中利用Python。Python别号为Guido Van Rossum的开拓职员创建。
Python一贯很随意马虎学习和节制。它非常适宜初学者,并且语法非常易于阅读和遵照。这无疑使我们所有人都愉快,令人惊奇的是python在环球拥有数百万快乐的学习者!
根据该网站的调查,Python的盛行度在2018年超过了C#–就像2017年超过了PHP。在GitHub平台上,Python超过了Java,成为第二大利用的编程措辞,与2017年比较,Python发出的拉取要求多40%在2016年。
这使 Python认证 成为最受欢迎的编程认证之一。
适用于初学者的Python项目| Python专案范例如何利用Python创建项目?这个问题的答案非常大略明了。这统统都始于学习Python的根本知识和所有根本知识。基本上,这是一个衡量指标,可以理解您利用Python的舒适程度。
下一步的紧张步骤是查看基本的大略代码,以熟习代码中的语法和逻辑流程。这是非常主要的一步,也为往后的发展奠定了坚实的根本。
现实生活中的Python?在此之后,您绝对该当查看python在现实生活中的用场。这将在找出为什么首先要学习Python的过程中扮演主要角色。
如果不是这种情形,那么您将理解项目,并可以为项目履行某些策略,您可以考虑自己开始。
其次肯定是要研究可以办理当前Python知识的项目。深入研究Python将有助于您在每个阶段进行自我评估。
项目基本上用于办理面前的问题。如果您喜好为各种大略和繁芜的问题供应办理方案,那么您绝对该当考虑从事Python项目。
在完成几个项目后,您将比精通python更近一步。这很主要,由于您将能够自发地将所学到的内容大略地编写为自己编写打算器程序,直至帮助实现人工智能。
我们可以用Python进行哪些项目?我们可以根据学习者的技能水平将Python项目分为初学者,中级和高等项目。
Python入门级项目Python子手游戏与Python利用Pygame的蛇游戏利用Python的科学打算器利用Python Flask的产品目标网页利用Python的URL缩短器Python中级项目利用Python进行网页爬取探索性数据剖析在Python中利用Kivy的Pong游戏利用Python Flask / Django Web框架的登录系统泰坦尼克号数据的生存预测Python高等项目利用OpenCV Python进行面罩检测利用Python进行语音识别利用Python进行笔墨转语音Python中的谈天机器人利用Selenium的Web浏览器自动化让我们从检讨Python项目的第一级开始。
Python初学者项目:利用Python的猜词游戏我们可以考虑的最好的初学者项目是Hangman游戏。我敢肯定,阅读此Python Projects博客的大多数人在您生命中的某个韶光点都曾玩过猜词。大略地说,这里的紧张目标是创建一个“猜词”游戏。听起来很大略,但是您须要把稳某些关键事变。
用户须要能够输入字母预测。还该当对可以利用的预测次数设置一个限定。连续将剩余的次数关照用户。这意味着您将须要一种获取单词以进行预测的方法。让我们保持大略,并利用文本文件作为输入。文本文件包含我们必须预测的单词。
您还将须要一些函数来检讨用户是否实际输入了单个字母,检讨输入的字母是否在隐蔽的单词中(如果是,显示了多少次),打印字母,以及一个计数器变量来限定预测。
Python根本起步
Python项目要记住的关键观点:
随机变数布尔型输入输出整数串长度打印代码:
Hangmanfrom string import ascii_lowercasefrom words import get_random_word def get_num_attempts(): """Get user-inputted number of incorrect attempts for the game.""" while True: num_attempts = input( 'How many incorrect attempts do you want? [1-25] ') try: num_attempts = int(num_attempts) if 1 <= num_attempts <= 25: return num_attempts else: print('{0} is not between 1 and 25'.format(num_attempts)) except ValueError: print('{0} is not an integer between 1 and 25'.format( num_attempts)) def get_min_word_length(): """Get user-inputted minimum word length for the game.""" while True: min_word_length = input( 'What minimum word length do you want? [4-16] ') try: min_word_length = int(min_word_length) if 4 <= min_word_length <= 16: return min_word_length else: print('{0} is not between 4 and 16'.format(min_word_length)) except ValueError: print('{0} is not an integer between 4 and 16'.format( min_word_length)) def get_display_word(word, idxs): """Get the word suitable for display.""" if len(word) != len(idxs): raise ValueError('Word length and indices length are not the same') displayed_word = ''.join( [letter if idxs[i] else '' for i, letter in enumerate(word)]) return displayed_word.strip() def get_next_letter(remaining_letters): """Get the user-inputted next letter.""" if len(remaining_letters) == 0: raise ValueError('There are no remaining letters') while True: next_letter = input('Choose the next letter: ').lower() if len(next_letter) != 1: print('{0} is not a single character'.format(next_letter)) elif next_letter not in ascii_lowercase: print('{0} is not a letter'.format(next_letter)) elif next_letter not in remaining_letters: print('{0} has been guessed before'.format(next_letter)) else: remaining_letters.remove(next_letter) return next_letter def play_hangman(): """Play a game of hangman. At the end of the game, returns if the player wants to retry. """ # Let player specify difficulty print('Starting a game of Hangman...') attempts_remaining = get_num_attempts() min_word_length = get_min_word_length() # Randomly select a word print('Selecting a word...') word = get_random_word(min_word_length) print() # Initialize game state variables idxs = [letter not in ascii_lowercase for letter in word] remaining_letters = set(ascii_lowercase) wrong_letters = [] word_solved = False # Main game loop while attempts_remaining > 0 and not word_solved: # Print current game state print('Word: {0}'.format(get_display_word(word, idxs))) print('Attempts Remaining: {0}'.format(attempts_remaining)) print('Previous Guesses: {0}'.format(' '.join(wrong_letters))) # Get player's next letter guess next_letter = get_next_letter(remaining_letters) # Check if letter guess is in word if next_letter in word: # Guessed correctly print('{0} is in the word!'.format(next_letter)) # Reveal matching letters for i in range(len(word)): if word[i] == next_letter: idxs[i] = True else: # Guessed incorrectly print('{0} is NOT in the word!'.format(next_letter)) # Decrement num of attempts left and append guess to wrong guesses attempts_remaining -= 1 wrong_letters.append(next_letter) # Check if word is completely solved if False not in idxs: word_solved = True print() # The game is over: reveal the word print('The word is {0}'.format(word)) # Notify player of victory or defeat if word_solved: print('Congratulations! You won!') else: print('Try again next time!') # Ask player if he/she wants to try again try_again = input('Would you like to try again? [y/Y] ') return try_again.lower() == 'y' if __name__ == '__main__': while play_hangman(): print()
2. Words.py
"""Function to fetch words.""" import random WORDLIST = 'wordlist.txt' def get_random_word(min_word_length): """Get a random word from the wordlist using no extra memory.""" num_words_processed = 0 curr_word = None with open(WORDLIST, 'r') as f: for word in f: if '(' in word or ')' in word: continue word = word.strip().lower() if len(word) < min_word_length: continue num_words_processed += 1 if random.randint(1, num_words_processed) == 1: curr_word = word return curr_word
输出如下:
后续
目前,理解了如何处理诸如Hangman之类的初学者项目,对其进行一些增强,然后开始下一个中级Python项目。欢迎关注我们获取更新。